Supabase Search Integration
The Supabase Search Integration in BuildShip empowers users to harness Supabase for their search and indexing requirements through a streamlined, low-code interface. Supabase provides efficient full-text search, semantic search, and hybrid search capabilities to create highly relevant search experiences within your applications and website.

Leveraging BuildShip's Supabase Nodes, users can seamlessly connect to their Supabase instances, unlocking the potential to craft APIs, Scheduled Jobs, and various backend workflows centered around search and indexing tasks. This integration is specially crafted to reduce the need for extensive coding, facilitating straightforward management of search indices, documents, and configurations within the intuitive BuildShip environment.
The Supabase Nodes provide a no-code interface for engaging with Supabase, ensuring a hassle-free integration of advanced search features into your projects. From indexing new documents and tweaking search settings to conducting intricate search queries, Supabase Nodes are designed to streamline these processes in a user-friendly manner.
Prerequisites ✅
Before you can start using the Supabase Nodes in BuildShip, ensure that you have the following prerequisites in place:
Supabase Project
You'll need access to a Supabase project. Follow these steps to prepare your account and initiate your first project:
- Navigate to Supabase (opens in a new tab) to either sign up for a new account or log in if you are an existing user.
- Create a new project and configure your database as needed.
It's important to note, generating API keys for secure interaction with your Supabase instance is an important step that follows the establishment of your project.
API Key
Supabase utilizes API keys to authenticate, granting complete operational access. For enhanced security, it is recommended to generate new API keys (opens in a new tab) with restricted scopes tailored to specific use cases.
Supabase provides two types of API keys. You can find more details in this API Key Documentation (opens in a new tab).
API URL
Supabase projects are uniquely identified by their API URL which you can retrieve from your project's API settings in the Supabase Dashboard. For more details on obtaining your Supabase instance's URL, refer to the Supabase documentation (opens in a new tab).
For comprehensive guidance on setting up the Supabase project, please refer to the Supabase Tutorial (opens in a new tab).
For the Full Text Search, Semantic Search, and Hybrid Search nodes, suppose you have a Supabase table called documents
with the columns id, title, content, and created_at. You can follow along with this guide to try out the nodes.
You can create the documents table with the following SQL code:
CREATE TABLE documents (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT NOT NULL,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);Add some sample data to the above table as described in the "Creating Data" (opens in a new tab) section.
Full Text Search
The "Full Text Search" node allows you to perform full-text searches on a Supabase table, enabling you to find documents that match a specific search query.
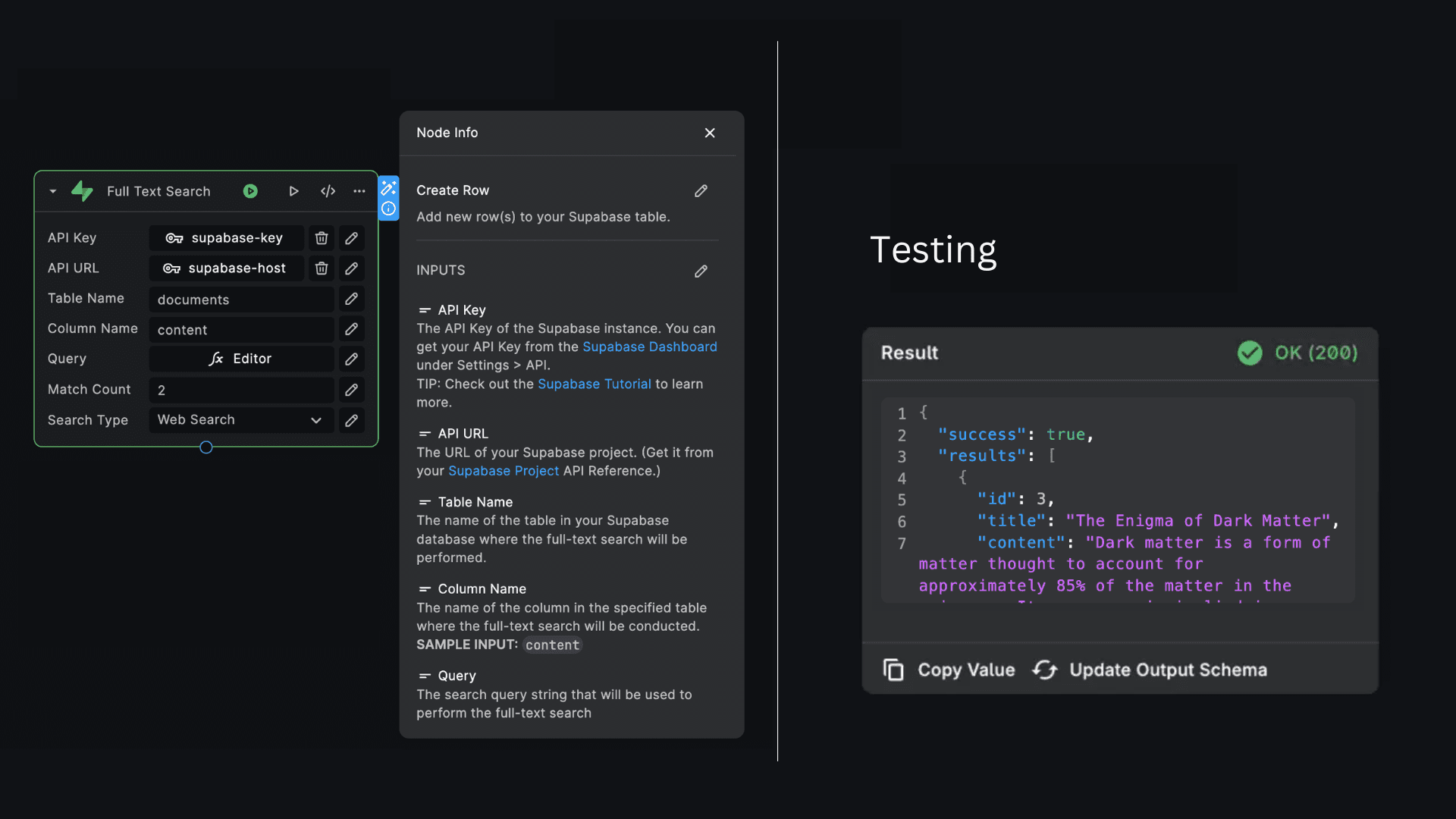
To set up supabase full text search in your BuildShip workflow, follow these steps:
Add Full Text Search Column
Add a full-text search (fts) column to the table you want to search within. Lets add a fts column to the documents
table which we have created earlier.
ALTER TABLE documents ADD COLUMN fts TSVECTOR GENERATED ALWAYS AS (to_tsvector('english', content)) STORED;TSVECTOR is a PostgreSQL data type used for storing text search vectors, which are optimized representations of text
for full-text search. This specifies that the fts column is a computed column, automatically generated based on the
content of another column (content in this case).
Create Index
Create an index for the full-text search.
CREATE INDEX ON documents USING gin(fts);This command creates an index on the fts column of the documents table. It allows fast lookups of documents that
contain specific words or phrases.
Adding a TSVECTOR column and creating a GIN index significantly enhances the performance of full-text search
queries by reducing the time and resources needed to find matching documents. By converting the content into a
TSVECTOR and indexing it, PostgreSQL can quickly identify relevant documents based on the search terms, making
searches much faster than scanning the entire table.
Inputs
-
API Key: The API key required for authentication with your Supabase instance. This should be provided as a secret.
-
API URL: The host address of your Supabase instance. This can be provided as a secret.
-
Table Name: The Supabase table name where you want to perform the search.
-
Column Name: The name of the column in the specified table where the full-text search will be conducted.
-
Query: The search query string that you want to use for finding matching documents.
-
Match Count: (Optional) The number of results to return. Default is 10.
-
Search Type: (Optional) The type of full-text search to perform. (
plain,phrase, andwebsearch)💡Use the "Full Text Search" node when you need to search for documents in a Supabase table based on a specific query. This can be useful in various scenarios, such as implementing search functionality in your application, finding relevant data based on user input, or filtering data based on specific criteria.
Output
The node returns an object with the following properties:
{
"success": boolean,
"results": [
{
"row": object
}
]
}success: A boolean value indicating the success of the operation.results: An array of objects, each representing an object that matched the search query. The row property contains the full row data.
Creating Embeddings
To perform semantic search hybrid search you need to create embeddings for your documents. Vectors in Supabase are
enabled via pgvector (opens in a new tab), a PostgreSQL extension for storing and querying vectors
in Postgres.It can be used to store embeddings (opens in a new tab). For
this you have to enable the vector extention which will give access to a new data type called vector. If you want
more information You can use this
guide (opens in a new tab)
to enable the extention. To enable it via sql command you can use below SQL code.
create extension vector
with
schema extensions;To create embeddings for your supabase table, follow these steps:
Add Embedding Column
Add an embedding column to the documents table:
ALTER TABLE documents ADD COLUMN embedding VECTOR(1536);Generate Embeddings
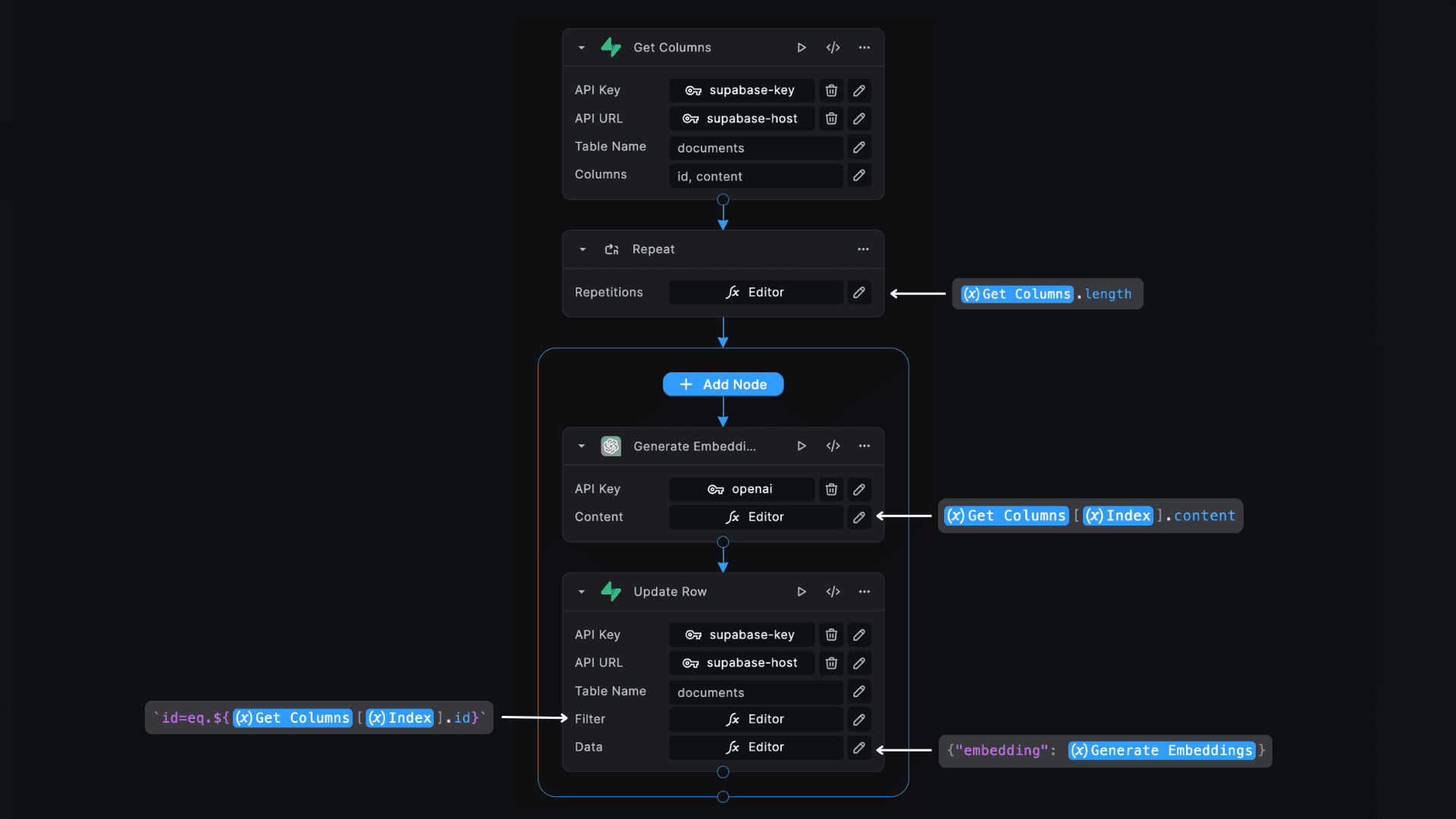
- Generate Embeddings with OpenAI: Use the Buildship OpenAI Generate Embeddings Node to create embeddings for each document's content.
- Retrieve Table Documents: Use the Get Columns node to retrieve all the documents from the table with the specified
columns. In this case, you only need the
idandcontentof each row. - Update Embedding Column: For each row, update the new embedding column value using the Generate Embeddings node and Supabase Update Row node enclosed in a Repeat node.
For a streamlined implementation, you can use this Remix template (opens in a new tab) as shown in the image below:
Semantic Search
Semantic search enables you to find documents that match the meaning of a search query. The Supabase "Semantic Search" node allows you to perform semantic searches on a Supabase table, enabling you to find documents that match the meaning of a search query.
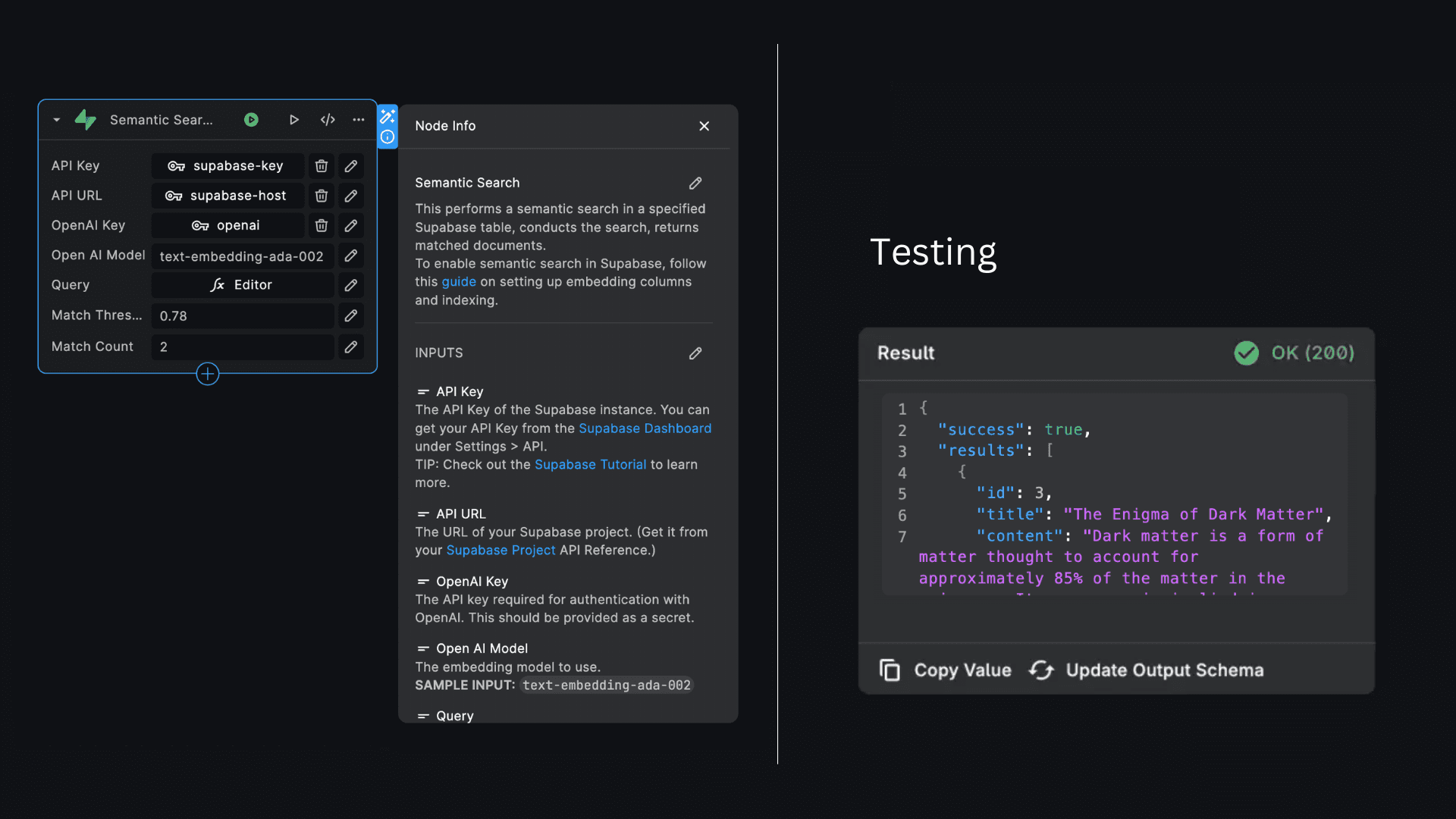
To set up supabase semantic search in your BuildShip workflow, follow these steps:
Create Index
To perform efficient semantic vector searches, you need to create an index on the embedding column in your table. This index uses the HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) algorithm, which is suitable for high-dimensional vector data.
Create an index for the semantic vector search:
CREATE INDEX ON documents USING hnsw (embedding vector_ip_ops);Semantic Search Function
To perform semantic search, you need to create a SQL function in your Supabase database to match rows based on
embeddings. This function will help you find rows that are semantically similar to the query. It is crucial that the
function is named semantic_search, as the node requires this specific name to operate correctly.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION semantic_search (
query_embedding VECTOR(1536),
match_threshold FLOAT,
match_count INT
)
RETURNS SETOF your_table
LANGUAGE SQL
AS $$
SELECT *
FROM your_table
WHERE your_table.embedding <=> query_embedding < 1 - match_threshold
ORDER BY your_table.embedding <=> query_embedding ASC
LIMIT LEAST(match_count, 200);
$$;In this example, replace your_table with the name of the table you are working with. The function will search for rows
within the specified table that are semantically similar to the provided query embedding.
Use the semantic_search function to perform semantic search queries. This function compares the embeddings stored in
the documents table with the embedding of the search query, returning documents that are semantically similar.
- Use the Semantic Search node to perform the search.
Inputs
- API Key: The API key required for authentication with your Supabase instance. This should be provided as a secret.
- API URL: The host address of your Supabase instance. This can be provided as a secret.
- OpenAI Key: The API key required for authentication with OpenAI. This should be provided as a secret.
- Open AI Model: The embedding model to use (e.g., 'text-embedding-ada-002').
- Query: The search query string that you want to use for finding matching documents.
- Match Threshold: (Optional) The threshold for matching results.
- Match Count: (Optional) The number of results to return.
Output
The node returns an object with the following properties:
{
"success": boolean,
"results": [
{
"row": object
}
]
}success: A boolean value indicating the success of the operation.results: An array of objects, each representing an object that matched the search query. The row property contains the full row data.
Hybrid Search
The Hybrid Search feature in Supabase combines traditional keyword search with semantic vector search, enabling you to find documents that are relevant both textually and semantically.The Supabase "Hybrid Search" node allows you to perform hybrid searches on a Supabase table, enabling you to find documents that match the meaning of a search query.
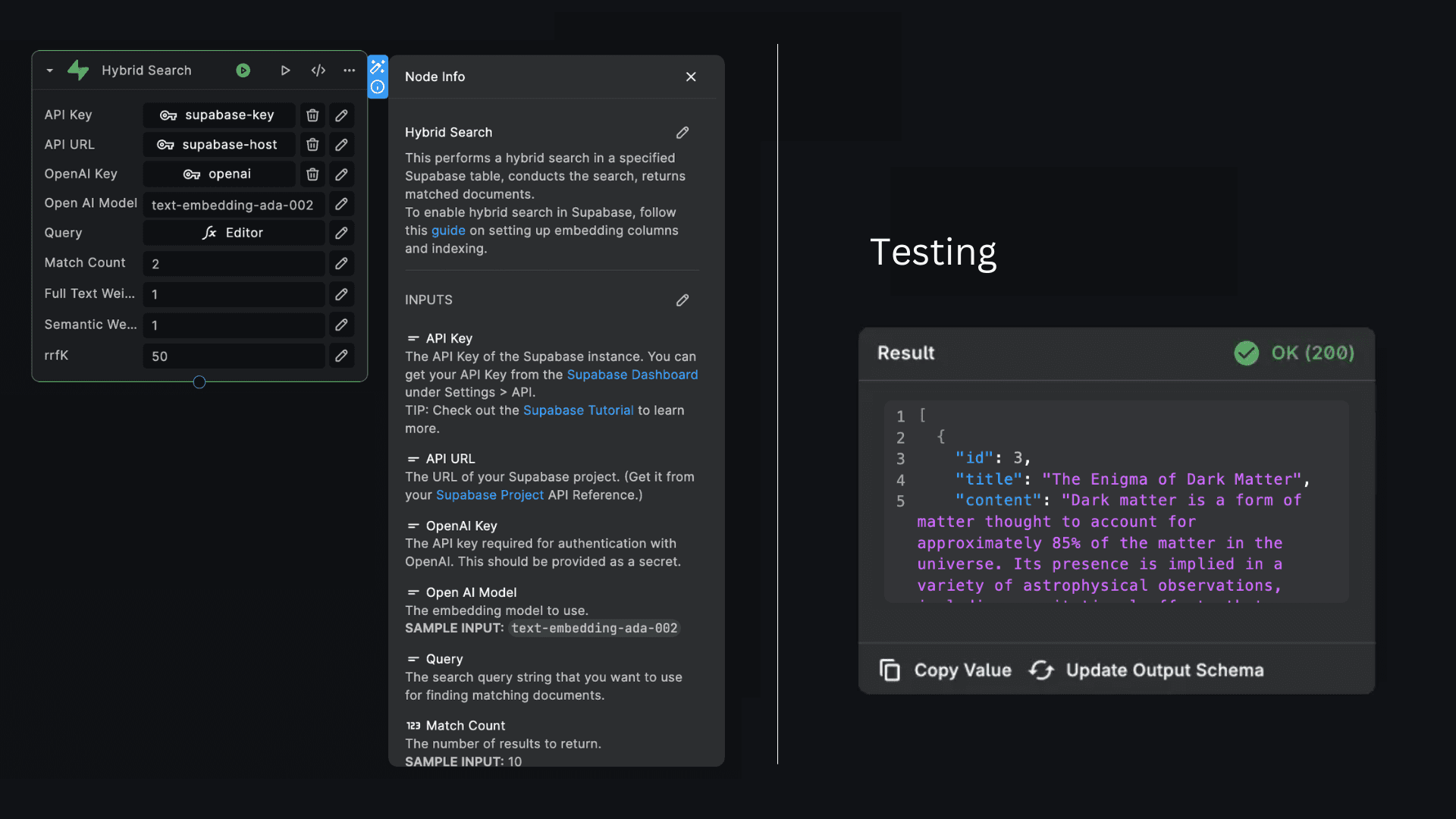
To set up supabase hybrid search in your BuildShip workflow, follow these steps:
Create the fts and embedding columns for the documents table as described in the Full Text Search and Semantic Search sections.
The table should look like below after adding fts and embedding columns:
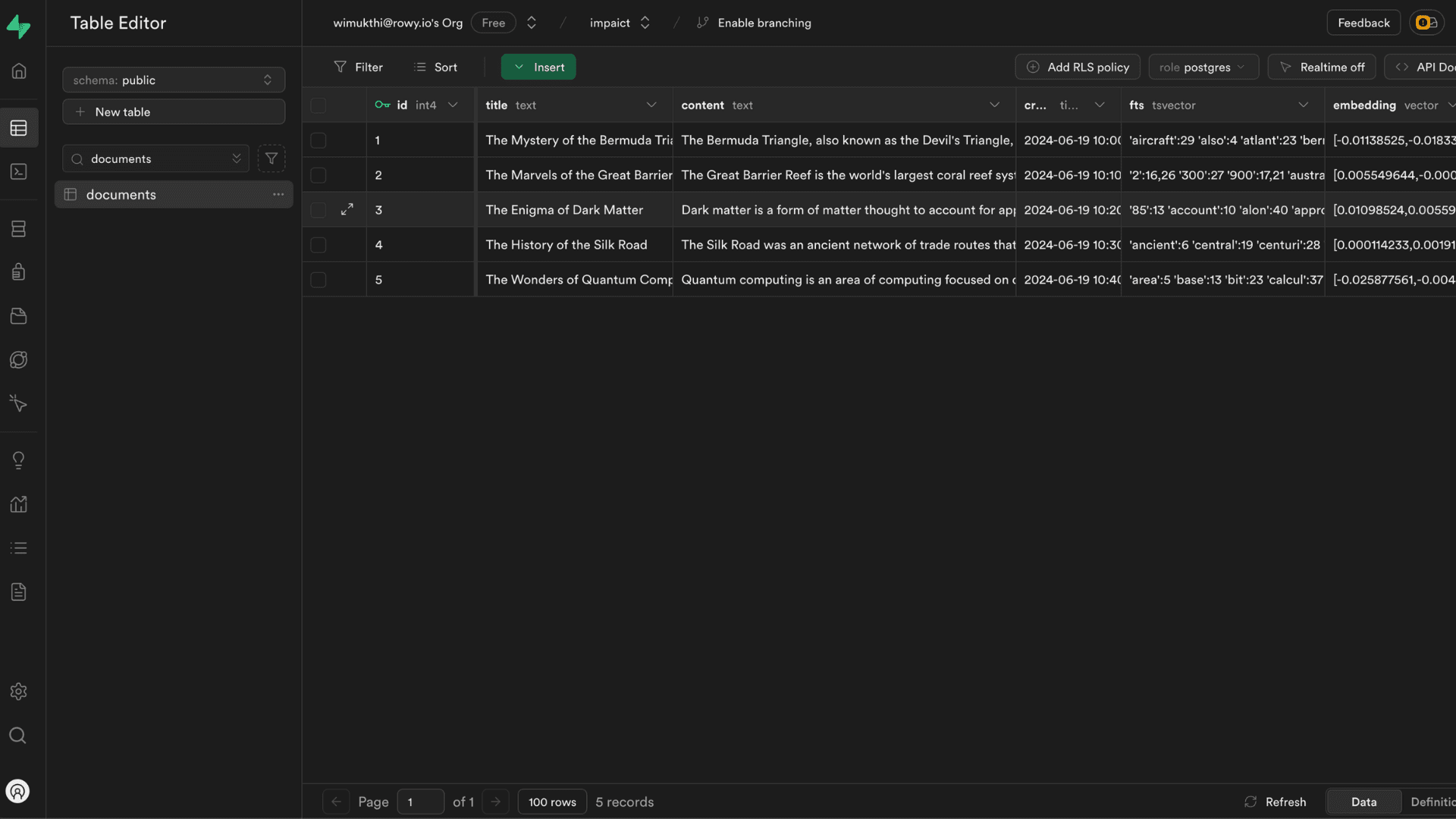
Hybrid Search Function
To perform hybrid search, you need to create a SQL function in your Supabase database to match rows based on embeddings
and full-text search. This function will help you find rows that are semantically and textually similar to the query. It
is crucial that the function is named hybrid_search, as the node requires this specific name to operate correctly.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION hybrid_search(
QUERY_TEXT TEXT,
QUERY_EMBEDDING VECTOR(1536),
MATCH_COUNT INT,
FULL_TEXT_WEIGHT FLOAT = 1,
SEMANTIC_WEIGHT FLOAT = 1,
RRF_K INT = 50
)
RETURNS SETOF your_table
LANGUAGE SQL
AS $$
WITH full_text AS (
SELECT id, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY ts_rank_cd(fts, websearch_to_tsquery(QUERY_TEXT)) DESC) AS rank_ix
FROM your_table
WHERE fts @@ websearch_to_tsquery(QUERY_TEXT)
LIMIT LEAST(MATCH_COUNT, 30) * 2
),
semantic AS (
SELECT id, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY embedding <#> QUERY_EMBEDDING) AS rank_ix
FROM your_table
LIMIT LEAST(MATCH_COUNT, 30) * 2
)
SELECT your_table.*
FROM full_text
FULL OUTER JOIN semantic ON full_text.id = semantic.id
JOIN your_table ON COALESCE(full_text.id, semantic.id) = your_table.id
ORDER BY
COALESCE(1.0 / (RRF_K + full_text.rank_ix), 0.0) * FULL_TEXT_WEIGHT +
COALESCE(1.0 / (RRF_K + semantic.rank_ix), 0.0) * SEMANTIC_WEIGHT
DESC
LIMIT LEAST(MATCH_COUNT, 30);
$$;In this example, replace your_table with the name of the table you are working with. The function will perform a
hybrid search within the specified table, combining both full-text search and semantic search to find rows that are
relevant to the provided query text and embedding.
Employ the "Hybrid Search" function to enhance search functionality in your applications by delivering results that not only match the keywords but also align semantically with the user's intent. This function is particularly beneficial in providing more relevant and context-aware search results, thereby improving the user experience.
- Use the Hybrid Search node to perform the search.
Inputs
- API Key: The API key required for authentication with your Supabase instance. This should be provided as a secret.
- API URL: The host address of your Supabase instance. This can be provided as a secret.
- OpenAI Key: The API key required for authentication with OpenAI. This should be provided as a secret.
- Open AI Model: The embedding model to use (e.g., 'text-embedding-ada-002').
- Query: The search query string that you want to use for finding matching documents.
- Match Count: The number of results to return.
- Full Text Weight: The weight for full-text search component in the hybrid search.
- Semantic Weight: The weight for semantic search component in the hybrid search.
- rrfK: The K constant for the Relative Ranking Factor (RRF) used in the search.
Output
The node returns an object with the following properties:
{
"success": boolean,
"results": [
{
"row": object
}
]
}success: A boolean value indicating the success of the operation.results: An array of objects, each representing an object that matched the search query. The row property contains the full row data.
Need Help?
- 💬Join BuildShip Community
An active and large community of no-code / low-code builders. Ask questions, share feedback, showcase your project and connect with other BuildShip enthusiasts.
- 🙋Hire a BuildShip Expert
Need personalized help to build your product fast? Browse and hire from a range of independent freelancers, agencies and builders - all well versed with BuildShip.
- 🛟Send a Support Request
Got a specific question on your workflows / project or want to report a bug? Send a us a request using the "Support" button directly from your BuildShip Dashboard.
- ⭐️Feature Request
Something missing in BuildShip for you? Share on the #FeatureRequest channel on Discord. Also browse and cast your votes on other feature requests.